DMP & DPIA
On this page, you can find more information about the Data Management Plan (DMP) and the Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA).
Data management plan (DMP)
Since 2016, all research projects must have a data management plan (DMP) before the start of the project. In a DMP, you capture which data and metadata will be collected, who is responsible for which tasks and what will happen to the (meta)data after the project has ended.
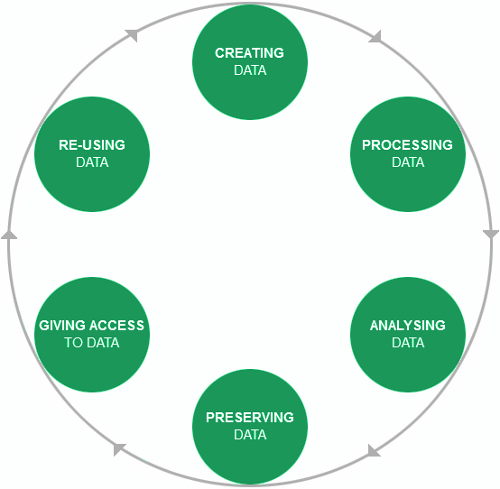
The research data lifecycle
Source: UK data archive
Components of a DMP
Fairly standard components of a DMP are:
- Cover information: project name, researchers, dates, ethical protocol numbers, etc.
- Data collection and creation
- How will you create your data?
- How will you access the data in the future?
- What license will you use?
- What kind of data will it be? E.g., how many and what type of files (see preferred file formats), how large (search for "file size calculator"), data quality (resolution, quality), usefulness (versions/processed or unprocessed)
- Data storage and security
- Where will you store your data?
- Where and how often will you make back-ups (1 copy offsite, 3 copies, 2 different media)?
- What do you do to make sure that the right people can access your data? (passwords, encryption, firewalls, anonymization, aggregation, secure transport and deletion, etc.)
- Documentation and metadata
- How are your files named and structured?
- Are you using version control?
- Are you providing readme files and/or other documentation? (e.g., time, place, people involved, etc.)
- Data access, sharing and reuse
- With whom do you want to share your data? How/where?
- Has ownership been agreed?
- Who might find your data useful later?
- Any restrictions regarding data sharing? Reasons to opt out of sharing with others: privacy / personal data (GDPR), intellectual property rights, might jeopardize the project’s main objective, commercial (working for companies), security-related, etc.
- Think about linking your data to your publication AND vice versa! Also think about linking your publications to you through an ORCID-ID
- Data preservation and archiving
- Which data do you want to keep for future use? Which data will you discard? Not all data necessarily need to be preserved!
- Where are you going to archive these data?
- How to organize the data so that they can still be understood in the future?
- Who is responsible for your data after you leave?
How to write a DMP?
At the EUR, you can use the DMP Online tool, which contains DMP templates of many funders, or use the EUR template.
- Create an account, select the (funder specific) format and simply fill out the form!
- If you leave the Funder field empty, you will use the general EUR-format.
- You can also invite colleagues to work on the DMP and leave comments
- Check your funder requirements: did they approve of the template you're using? E.g., if your research is funded by NWO, you have to use one of their approved templates and get feedback from an expert (see contacts below)
Read more about DMPs at the EUR, EUR guidelines and the EUR template here.
Need examples? See this page for a collection of publicly available DMPs.
Data protection impact assessment (DPIA)
Whenever you process sensitive data (or something changes regarding this), such as MRI data, names, addresses, daily diaries, etc., you are required to fill in a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) that has to be approved before starting your study by a privacy officer. In a DPIA, you identify privacy risks and formulate measures to prevent breaches. You register which data you collect and who is responsible. A DPIA touches upon:
- Collaborations in your project:
- Within your institute
- Between institutes: agree upon who has access to the data and which technologies are used (e.g., for saving and analyzing the data)
- Public-private collaborations: make contractual agreements about how to handle data
- Geography: outside of the EU, you need to make contractual agreements about how to handle data
- Types of data collected:
- Automatically generated (e.g., fitness watches)
- Own creation, e.g., interviews, pictures
- Re-used, e.g., multiple datasets combined (pay attention to identifiability)
Resources
Contacts
- For checking your (ESSB) DMP and/or DPIA, contact the faculty data steward
- For general questions about DMPs and DPIAs, contact the Erasmus Data Service Center (EDSC): edsc [at] eur [dot] nl
- EDSC workshop agenda
- For the DPIA, contact the ESSB privacy officer (privacy [at] essb [dot] eur [dot] nl)
Resources
- Core requirements for the DMP (p.11+12) by the NWO and others
- More information about data management (storing, archiving, versioning, data structure, etc.) and backing up and versioning data
- How to name your files
- The costs of data management
- More about privacy and legal aspects
- Leiden University DPIA template